CONTEST: Are those puppies I see?
John Cuzzola, October 23, 2023
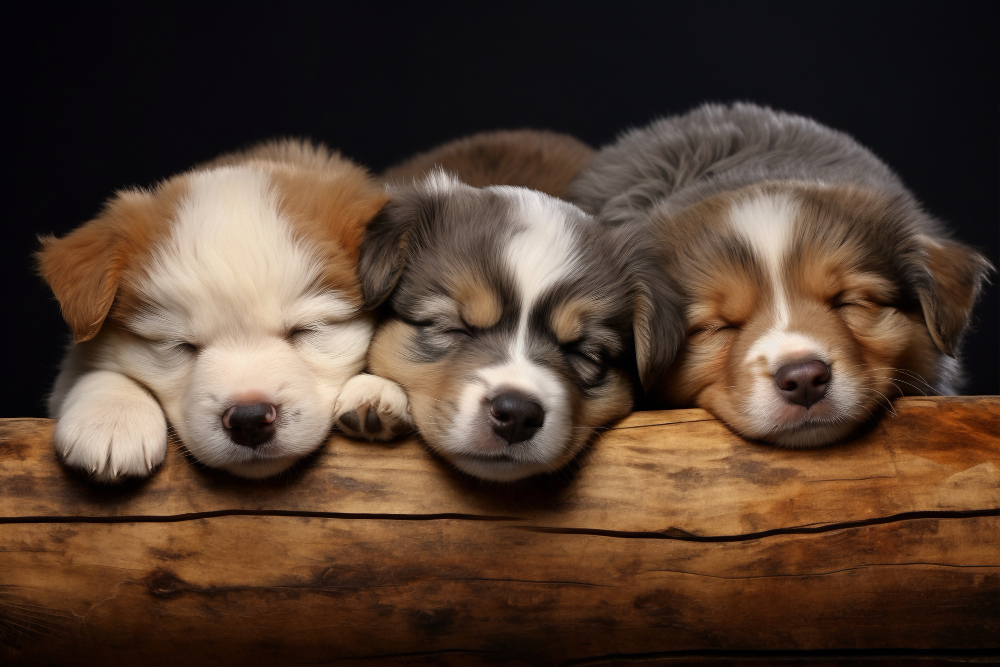

Imagine you're a child and you have a secret message you want to share with a friend, but you don't want anyone else to know about it. Instead of handing your friend a note with the message (which could be easily found), you decide to write it in invisible ink on a regular drawing. To anyone else, it looks like a normal drawing. But you and your friend know the secret, so with a special light, you can read the message.
In Cybersecurity, this technique is called steganography. It is commonly used for adversaries to “smuggle” information out of an organization in seemingly innocent ways (like through a picture of cute puppies); or for secret communication between parties by hiding the message in clear sight. Steganography comes from the two Greek words: "steganos" which means "covered" or "concealed", and "graphein" which means "to write".
Least Significant Bit (LSB) Encoding:
This might sound like magic, but it's actually quite simple when you understand how pictures are stored in computers. Every digital photo is made up of tiny dots called pixels. Each pixel has a color, and this color is represented by a set of numbers in the computer usually red, green, and blue often referred to as RGB. Each set has a range between zero (0) and 255. To keep things simple, let's consider only the blue set. A blue pixel value of zero means very very dark blue – actually the color is so dark it’s black. A blue value of 255 is a very bright shade of blue and a value of 128 is a shade somewhere in between these extremes. The human eye can differentiate approximately 10 million colors. Suppose you have a pixel with blue color code 86. Do you think your eye can distinguish the shade of blue represented by 85 or 87 as a different shade to 86?
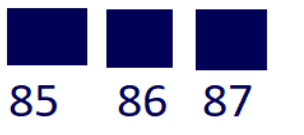
In reality, this difference of 1 is indistinguishable to your eye so the picture you are seeing looks just fine. However, a computer can tell the difference, and it’s this 1-bit difference (also known as least significant bit), that a message can be embedded in the image simply by manipulating these color shades by a small value. So here's the trick: instead of using the true color code shade of a pixel, we can swap it out for a value slightly larger or smaller that maps to one bit from our secret message (either a binary 0 or 1). Because it's such a tiny change, our eyes can't see the difference, but the message is hidden right there in plain sight! By doing this with many pixels in the photo, bit by bit, we can hide a whole message. Only someone who knows the trick (like you and your friend) can extract the secret message from the picture.
Try it for Yourself
This blog started with a picture of a cute trio of puppies, but as the Transformers would say “there’s more than meets the eye”. Follow these steps:
- Right-click on the puppies, and select “SAVE IMAGE AS” or similar option. The goal is to save a copy of the image to your hard drive. Do not change the file type or any other settings.
- Go to this site: https://stegtool.net/
- Select the DECODE tab, upload your puppy image from step 1, and press the DECODE IMAGE button. If you followed these steps accurately, the message hidden inside the image will be revealed.
- Follow the instructions given by the secret message to enter a draw for a prize!!!
Week 3 of Cybersecurity Awareness Month
Why You Need a Password Manager at TRU
Taylar Masson, Oct 16, 2023
October is Cybersecurity Awareness Month, a time to learn more about the importance of staying safe online. One of the most essential steps you can take to protect yourself and your institution is to use a password manager.
A password manager is a software tool that securely stores and manages your passwords for different online accounts. It can also help you create and remember strong, unique passwords for each site you use.
Using a password manager has many benefits for students and staff at TRU, such as:
- Enhancing your security: Password managers protect your passwords from hackers, phishing, and data breaches. They also alert you of any weak or compromised passwords and help you change them easily.
- Saving your time: Password managers autofill your login credentials on websites, so you don’t have to type them manually or remember them. They also sync your passwords across your devices, so you can access them anytime, anywhere.
- Reducing your stress: Password managers eliminate the hassle of forgetting or resetting your passwords. They also let you share passwords securely with others when needed, such as for group projects or work assignments.
How to Choose a Password Manager
There are many password managers available on the market, but not all of them are equally reliable or suitable for higher education. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a password manager:
- Security: Look for a password manager that uses strong encryption, zero-knowledge architecture, and multi-factor authentication. These features ensure that only you can access your passwords and that they are not stored in plain text or shared with anyone else.
- Features: Look for a password manager that offers the functionality you need, such as password generator, password audit, password sharing, dark web monitoring, VPN, etc. These features can help you improve your password hygiene and online privacy.
- Usability: Look for a password manager that is easy to use and compatible with your devices and browsers. You should be able to install it quickly, set it up smoothly, and use it intuitively.
- Cost: Look for a password manager that fits your budget and offers good value for money. Some password managers are free, while others charge a monthly or yearly fee. Compare the features and benefits of different plans and choose the one that meets your needs.
Some Recommended Password Managers
There is an ever growing list of password managers to choose from. PCMag keeps an updated list of their recommendations, you can find that here. There is no one manager we recommend as everyone has their own needs, but here are a few you may consider:
- Dashlane: Dashlane is a premium password manager that offers advanced security and privacy features, such as VPN and dark web monitor. It also has a user-friendly interface and supports multiple platforms and browsers.
- Zoho Vault: Zoho Vault is a password manager that focuses on password sharing and collaboration. It allows you to create and manage groups of users and share passwords securely with them. It also integrates with other Zoho products and popular cloud services.
- Bitwarden: Bitwarden is a free and open source password manager that offers basic but essential features, such as password generator, password audit, and multi-device sync. It also has a simple and clean interface and supports various platforms and browsers.
How to Use a Password Manager Effectively
Once you have chosen a password manager, here are some tips on how to use it effectively:
- Create a master password: Your master password is the key to unlock your password vault, so make sure it is strong and memorable. You can use a passphrase or a combination of letters, numbers, symbols, and spaces. Do not use the same master password for other accounts or share it with anyone else.
- Import your existing passwords: Most password managers allow you to import your existing passwords from your browsers or other sources. This can save you time and effort in transferring your passwords to your new tool. However, you should also review your imported passwords and update any weak or duplicate ones.
- Generate new passwords: Whenever you create a new account or change an old password, use the password generator feature of your password manager to create a strong and unique password. You can customize the length and complexity of your passwords according to the site’s requirements.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring something else besides your password to log in, such as a code or a biometric. You should enable MFA for both your password manager account and any other sensitive accounts you have.
- Update your passwords regularly: Even if you have strong passwords, you should change them periodically to prevent them from being compromised or outdated. You can use the password audit feature of your password manager to check the age and strength of your passwords and change them accordingly.
Conclusion
Using a password manager is one of the best ways to protect your online accounts and personal information. It can also make your life easier and more productive by saving you time and hassle. By following the tips and recommendations in this article, you can choose and use a password manager that suits your needs and preferences.
We hope you found this article helpful and informative. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to contact us. And don’t forget to check out our other resources for Cybersecurity Awareness Month at TRU. Stay safe and stay cyber fit!
How to Protect Your Online Accounts from Credential Stuffing Attacks
Taylar Masson, Oct 16, 2023
Credential stuffing is a type of cyberattack that uses stolen usernames and passwords from data breaches to access other online accounts. It is a serious threat because many people reuse the same passwords across different websites, making it easy for hackers to take over their accounts.
In this article, we will explain what credential stuffing is, how it works, and how you can prevent it by using services such as HaveIBeenPwned and creating strong, unique passwords for every account.
What is Credential Stuffing?
Credential stuffing is the automated injection of breached username/password pairs in order to fraudulently gain access to user accounts. This is a subset of the brute force attack category: large numbers of spilled credentials are automatically entered into websites until they are potentially matched to an existing account, which the attacker can then hijack for their own purposes.
Credential stuffing attacks are one of the most common ways cybercriminals abuse stolen usernames and passwords. This is a brute-force attack technique, but instead of trying to guess passwords using “dictionaries” of common word combinations, attackers use lists of known valid credentials obtained from data breaches.
Credential stuffing attacks are very effective because many people use the same password or a few variations of it for multiple online accounts. According to a study by Google, 52% of users reuse the same password for multiple accounts and 13% of users reuse the same password for all their accounts. This means that if one of your accounts is compromised in a data breach, all your other accounts that use the same password are at risk of being hacked as well.
How Does Credential Stuffing Work?
Credential stuffing attacks usually follow these steps:
- The attacker obtains a list of email addresses and passwords from a data breach or other sources. These lists are often sold or shared on the dark web or hacking forums.
- The attacker uses a tool or a botnet to automate the process of trying different combinations of usernames and passwords on various websites. The tool or botnet can bypass security measures such as CAPTCHAs or rate limits by using proxies or rotating IP addresses.
- The attacker identifies which credentials are valid for each website and collects them in a database. The attacker can then use these credentials to access the user’s account, steal personal information, perform fraudulent transactions, send spam, or launch further attacks.
How Can You Prevent Credential Stuffing?
The best way to prevent credential stuffing attacks is to use strong, unique passwords for every online account. A strong password is one that is long, complex, and random, and that does not contain any personal or common information. A unique password is one that is not used for any other account or service.
To create and manage strong, unique passwords, you can use a password manager. A password manager is a software application that securely stores your passwords and generates new ones for you. You only need to remember one master password to access your password manager and all your other passwords.
Another way to prevent credential stuffing attacks is to use services such as HaveIBeenPwned. HaveIBeenPwned is a website that allows you to check if your email address or password has been exposed in a data breach. You can also subscribe to receive notifications if your email address appears in future breaches. If you find out that your email address or password has been compromised, you should change it immediately and check your other accounts for suspicious activity.
Additionally, you can enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for your online accounts whenever possible. MFA is a security feature that requires you to provide more than one piece of evidence to verify your identity when logging in. For example, you may need to enter a code sent to your phone or email, scan your fingerprint, or use an app like Google Authenticator. MFA adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts and makes it harder for hackers to access them even if they have your credentials.
Conclusion
Credential stuffing is a serious cyberattack that exploits the password reuse problem. It can result in identity theft, financial loss, privacy violation, and other damages. To protect yourself from credential stuffing attacks, you should use services such as HaveIBeenPwned to check if your credentials have been exposed in data breaches, use strong, unique passwords for every online account, use a password manager to create and manage your passwords, and enable multi-factor authentication for your accounts.
By following these tips, you can improve your online security and reduce the risk of credential stuffing attacks.
Week 2 of Cybersecurity Awareness Month
Enhanced Password Standards: Strengthening Security at TRU
Vivian Oosthoek, Oct 10, 2023
At Thompson Rivers University (TRU), we are committed to safeguarding your digital security. As part of our ongoing efforts to protect your personal information and ensure the integrity of our systems, we are proud to announce significant updates to our password standards, effective as of August of this year. These changes are designed to enhance your online safety and minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Key Updates to Password Standards:
- Increased Minimum Password Length: We've raised the bar for password complexity by increasing the minimum password length from 8 characters to a more robust 12 characters. This longer character requirement helps create stronger, more resilient passwords.
- Comprehensive Character Requirements: To further fortify your passwords, we now mandate the use of a combination of lowercase letters, uppercase letters, numeric digits, and symbol characters. This diverse mix of characters makes it considerably more challenging for unauthorized parties to crack your password.
- Elimination of Regular Expirations: In our commitment to user convenience, we have eliminated the routine password expiration policy, as we now have MFA as a secondary layer of protection against account compromise. Your password will only expire if your account is implicated in a security incident. Previously, staff members were required to update their passwords every 6 months, while students had to do so annually. Now, you'll only need to update your password if there's a legitimate security concern.
Why These Changes Matter:
These updates reflect our commitment to continuously improving your digital security. Passwords serve as the first line of defense against cyber threats, and by strengthening our password standards, we reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. These measures not only protect you but also contribute to a safer and more secure digital environment for our entire TRU community.
At TRU, your online safety is our top priority. Our enhanced password standards, including increased complexity requirements and the elimination of regular expirations, are designed to provide you with peace of mind when it comes to protecting your digital identity and sensitive information.
Enhancing TRU's Security with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Taylar Masson, Oct 10, 2023
We are excited to announce an important security enhancement for your accounts at TRU. Recently, we have enabled Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all student accounts accessing Microsoft services, including email and the Office suite. In this blog post, we will explain what MFA is, why it matters, how we are implementing it, and where you can find resources to manage your account effectively.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
MFA is a security feature that adds an extra layer of protection to your account. Instead of relying solely on a password, MFA requires you to provide an additional form of verification during sign-in. This could be a text message code, a phone call, or a mobile app notification. By using MFA, we significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access even if your password is compromised.
Why is MFA Important?
- Enhanced Security: With MFA, even if someone gets hold of your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second factor (e.g., your phone).
- Protection Against Phishing: MFA prevents attackers from gaining access through phishing attacks.
- Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory standards now mandate the use of MFA to protect sensitive data.
How We are Implementing MFA
Enforced for All Students
- MFA is now mandatory for all TRU student accounts. When you sign into Microsoft services, you will be prompted to set up MFA. This added layer of security ensures that even if your password is compromised, unauthorized access is prevented.
Where MFA Is Needed
- On-Campus Access: When signing in from TRU campus locations, MFA will not be mandatory.
- Off-Campus Access: For security reasons, MFA remains enforced when accessing your account remotely.
Easy Setup
- Setting up MFA is straightforward:
- Sign into any Microsoft service (e.g., Outlook, Teams).
- Follow the prompts to choose your preferred verification method:
- Text message
- Phone call
- Mobile app notification
- Complete the setup process.
Remember Your Device
- Once you have set up MFA on a device (e.g., laptop, smartphone), you will not need to verify again unless you switch to a new device, browser, or have been inactive for more than a month.
- Remember that this convenience also means safeguarding your device against unauthorized use.
Managing Your Account
- To set up or manage student MFA settings: https://aka.ms/mfasetup
- For any issues or questions related to MFA: Contact our IT support team at itservicedesk@tru.ca
- Learn more about MFA: Visit our MFA Knowledge Base https://tru.teamdynamix.com/TDClient/84/Portal/KB/ArticleDet?ID=6714
Upcoming Changes
As part of our commitment to enhancing the security of our digital environment, we plan to extend MFA to other key services soon. Here is what you can expect:
Moodle
Our Learning Management System, Moodle, will soon require MFA for sign-in. This will ensure that only you can access your courses, grades, and other academic resources.
MYTRU
MyTRU, your portal for registration, financial aid, personal information, and other student services, will also be adopting MFA. This will add an extra layer of protection to your personal and academic records.
VPN
For those who access our network remotely via VPN, MFA will be implemented to prevent unauthorized access. This is especially important as VPN provides access to internal resources that are otherwise inaccessible from outside our network.
Passwordless Authentication
- Your Microsoft account offers what is called “Passwordless sign-in". For those with Microsoft MFA setup on the Microsoft Authenticator you can enable this option in the App. You may also elect to add a hardware token to use this (Such as a “Yubikey”).
- Passwordless authentication lets you sign in, as it suggests, without using your password. Having your phone (Something you have), combined with biometrics (Something you are) or PIN code (Something you know) cover the “multiple factors” in MFA and is more secure than a password, which could be easily guessed or stolen.
- DUO MFA for employees does not currently support this. This option will become available in the near future.
You will not have to do anything as part of these changes. All services will use your Microsoft account and be protected by the same MFA you set up now.
Remember that security is a shared responsibility. By using MFA, you play an active role in safeguarding your account and our institution’s data.
Thank you for helping us create a more secure digital environment at TRU!
Embrace the Power of VPNs - but Beware of the Slow Lane
Obiora Akachukwu, October 10, 2023
We live in an age where staying connected is crucial, and that often means hopping onto public Wi-Fi networks. Whether you're at a coffee shop, the library, or an airport, free public Wi-Fi is a lifesaver. But it comes with risks—risks that can be mitigated with a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over the internet, allowing users to access the internet as if they were connected to a private network. A VPN is like your own secret tunnel in the digital world.
Let's dive into the benefits of incorporating VPNs into your online routine.
Benefits
- Enhanced Privacy and Security
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, making it incredibly difficult for hackers or prying eyes to intercept your online activities. This is particularly valuable when accessing public Wi-Fi networks, which are notorious for their lack of security. For students and faculty handling sensitive academic data, this level of protection is a game-changer.
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
VPNs allow you to appear as though you're browsing the internet from a different location. This means you can access online resources or educational content that may be restricted or blocked in your region, broadening your research and learning possibilities.
- Secure File Sharing
VPNs create a secure tunnel for data transfer, making file sharing and collaboration safer and more confidential. This is particularly useful for faculty members working on research projects or students engaged in group assignments.
- Anonymity and Reduced Tracking
VPNs mask your IP address, reducing the ability of websites and advertisers to track your online behavior. This can enhance your online privacy and reduce the amount of targeted advertising you encounter.
- Access to Institutional Resources
Universities and colleges like TRU sometimes limit access to their resources from off-campus locations. A VPN can provide a secure way to connect to the university's network remotely, giving faculty and students access to library resources, academic databases, and other services even when not on campus. TRU offers access to the GlobalProtect VPN for this very purpose.
In conclusion, VPNs offer valuable advantages for both students and faculty, especially when it comes to online security and privacy. However, they are not without their drawbacks, including potential speed reductions and the need to trust a third-party provider when not using the university-provided VPN solution. When deciding whether to use a VPN, consider your specific needs and the potential benefits and limitations in the context of your online activities.
Protect Your Identity Information!
Kevin Zhong, Oct 10, 2023
Identity theft happens when someone uses your personal data, such as your name, birthday, social insurance number, to impersonate you. Identity thieves may steal money from your bank accounts, open new credit cards, or get utility services under your name, steal your tax refund, use your insurance information to receive medical treatments, or give police your name and address when they are arrested.
There are ways to protect yourself from identity theft:
- Change your password regularly and use two-factor authentication.
- Do not keep extra credit cards, or your Social Insurance Card, birth certificate, or passport with you unless necessary.
- Freeze your credit with the two major credit bureaus in Canada, Equifax and TransUnion, so that most lenders cannot obtain your credit report, therefore new credit files cannot be opened under your identity. It is free to freeze and unfreeze your credit.
- Keep a list of all your credit and bank accounts in a secure place so you can quickly call the issuers to inform them about missing or stolen cards. Your list should include account numbers, expiration dates, and customer service and fraud department telephone numbers.
- Take your credit/debit and ATM card receipts with you. Do not toss them and pre-approved credit offers, credit card or utility bills in your trash or recycling bin without first tearing them into small pieces or shredding them.
- Do not give credit card, bank, or Social Insurance Number information to anyone by telephone, even if you made the call, until you can verify that the call is legitimate.
- Avoid any offer that sounds too good to be true – they are often scams. Be very skeptical of offers that require your Social Insurance Number, credit, or financial information as an enrollment condition.
How do I know if I’m a victim of identity theft?
- Scrutinize your credit card statement, utility, and subscription bills to ensure the charges are yours.
- One of your creditors informs you that they have approved or declined your application that you have never applied for.
- A collection agency contacts you to collect on your defaulted account, when you never opened that account.
What should I do if I suspect that I’m a victim of credit fraud?
- Reconcile your cheque and credit card statements regularly and challenge any purchases you did not make.
- Report all stolen credit cards immediately to the issuers and request new cards.
- If you are a victim of a data breach, ask the credit bureaus (Equifax and TransUnion in Canada) to place a fraud alert on your credit files. Lenders will need to contact you and confirm your identity before they approve any application for credit under your identity.
- Contact your local police to file a complaint after a data breach.
- Report any fraud to the Canadian Anti-Fraud Center (CAFC). The CAFC is a national police service that assists Police of Jurisdiction. It is Canada’s central repository for information about fraud.
- Notify Canada Post Postal Security if you suspect your mail was stolen.
Week 1 of Cybersecurity Awareness Month
Blocking Spam and Protecting Your University Inbox: The Power of Microsoft Spam Filtering and DMARC
Obiora Akachukwu, Oct 3, 2023
Today, let’s chat about something that's both annoying and potentially harmful: spam emails.
In June of 2023, the Information Technology Services implemented Microsoft's advanced spam filtering technology and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) to make our university email experience way safer and smoother. Let's dive into the world of these new email standards and see how they're protecting our inboxes.
1. Microsoft Spam Filtering: Your Email Bouncer
You know those pesky spam emails that clutter your inbox? They're like party crashers at your favorite hangout. Microsoft's spam filtering technology is like the bouncer who keeps the undesirables out. It uses smart algorithms to spot spammy emails and sends them straight to the digital trash bin. No more sifting through shady promotions or suspicious offers.
2. DMARC: The Ultimate Identity Checker
DMARC is like the digital passport control at the airport but for emails. It helps ensure that the emails you receive are from who they claim to be from. Cybercriminals often try to impersonate trusted sources, like your employer, to trick you into revealing sensitive information. DMARC verifies the authenticity of the sender's domain, making it much harder for email scammers to sneak in.
3. Reduced Phishing Risks
Phishing attacks are like digital fishing expeditions where scammers try to hook you with fake emails. These can be seriously dangerous, especially for students and faculty dealing with academic and personal data. Microsoft's spam filtering and DMARC combo work together to spot phishing emails and protect your personal info and login credentials.
4. Enhanced Email Security
In the age of cyber threats, keeping your email secure is a top priority. Microsoft's robust spam filtering technology and DMARC help guard our university communications like a fortress. You can collaborate, share research, and communicate without worrying about email security breaches.
So, there you have it, folks. Microsoft's spam filtering technology and DMARC are like the dynamic duo of email security, making sure your university inbox is clean, safe, and hassle-free. You can focus on your studies, research, and teaching without spending as much time worrying about the distraction of spam or the fear of email scams. It's like having a digital guardian for your university email, which is a great perk.
Why You Need a Password Manager at TRU
Taylar Masson, Oct 16, 2023
October is Cybersecurity Awareness Month, a time to learn more about the importance of staying safe online. One of the most essential steps you can take to protect yourself and your institution is to use a password manager.
A password manager is a software tool that securely stores and manages your passwords for different online accounts. It can also help you create and remember strong, unique passwords for each site you use.
Using a password manager has many benefits for students and staff at TRU, such as:
- Enhancing your security: Password managers protect your passwords from hackers, phishing, and data breaches. They also alert you of any weak or compromised passwords and help you change them easily.
- Saving your time: Password managers autofill your login credentials on websites, so you don’t have to type them manually or remember them. They also sync your passwords across your devices, so you can access them anytime, anywhere.
- Reducing your stress: Password managers eliminate the hassle of forgetting or resetting your passwords. They also let you share passwords securely with others when needed, such as for group projects or work assignments.
How to Choose a Password Manager
There are many password managers available on the market, but not all of them are equally reliable or suitable for higher education. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a password manager:
- Security: Look for a password manager that uses strong encryption, zero-knowledge architecture, and multi-factor authentication. These features ensure that only you can access your passwords and that they are not stored in plain text or shared with anyone else.
- Features: Look for a password manager that offers the functionality you need, such as password generator, password audit, password sharing, dark web monitoring, VPN, etc. These features can help you improve your password hygiene and online privacy.
- Usability: Look for a password manager that is easy to use and compatible with your devices and browsers. You should be able to install it quickly, set it up smoothly, and use it intuitively.
- Cost: Look for a password manager that fits your budget and offers good value for money. Some password managers are free, while others charge a monthly or yearly fee. Compare the features and benefits of different plans and choose the one that meets your needs.
Some Recommended Password Managers
There is an ever growing list of password managers to choose from. PCMag keeps an updated list of their recommendations, you can find that here. There is no one manager we recommend as everyone has their own needs, but here are a few you may consider:
- Dashlane: Dashlane is a premium password manager that offers advanced security and privacy features, such as VPN and dark web monitor. It also has a user-friendly interface and supports multiple platforms and browsers.
- Zoho Vault: Zoho Vault is a password manager that focuses on password sharing and collaboration. It allows you to create and manage groups of users and share passwords securely with them. It also integrates with other Zoho products and popular cloud services.
- Bitwarden: Bitwarden is a free and open source password manager that offers basic but essential features, such as password generator, password audit, and multi-device sync. It also has a simple and clean interface and supports various platforms and browsers.
How to Use a Password Manager Effectively
Once you have chosen a password manager, here are some tips on how to use it effectively:
- Create a master password: Your master password is the key to unlock your password vault, so make sure it is strong and memorable. You can use a passphrase or a combination of letters, numbers, symbols, and spaces. Do not use the same master password for other accounts or share it with anyone else.
- Import your existing passwords: Most password managers allow you to import your existing passwords from your browsers or other sources. This can save you time and effort in transferring your passwords to your new tool. However, you should also review your imported passwords and update any weak or duplicate ones.
- Generate new passwords: Whenever you create a new account or change an old password, use the password generator feature of your password manager to create a strong and unique password. You can customize the length and complexity of your passwords according to the site’s requirements.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring something else besides your password to log in, such as a code or a biometric. You should enable MFA for both your password manager account and any other sensitive accounts you have.
- Update your passwords regularly: Even if you have strong passwords, you should change them periodically to prevent them from being compromised or outdated. You can use the password audit feature of your password manager to check the age and strength of your passwords and change them accordingly.
Conclusion
Using a password manager is one of the best ways to protect your online accounts and personal information. It can also make your life easier and more productive by saving you time and hassle. By following the tips and recommendations in this article, you can choose and use a password manager that suits your needs and preferences.
We hope you found this article helpful and informative. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to contact us. And don’t forget to check out our other resources for Cybersecurity Awareness Month at TRU. Stay safe and stay cyber fit!
How to Protect Your Online Accounts from Credential Stuffing Attacks
Taylar Masson, Oct 16, 2023
Credential stuffing is a type of cyberattack that uses stolen usernames and passwords from data breaches to access other online accounts. It is a serious threat because many people reuse the same passwords across different websites, making it easy for hackers to take over their accounts.
In this article, we will explain what credential stuffing is, how it works, and how you can prevent it by using services such as HaveIBeenPwned and creating strong, unique passwords for every account.
What is Credential Stuffing?
Credential stuffing is the automated injection of breached username/password pairs in order to fraudulently gain access to user accounts. This is a subset of the brute force attack category: large numbers of spilled credentials are automatically entered into websites until they are potentially matched to an existing account, which the attacker can then hijack for their own purposes.
Credential stuffing attacks are one of the most common ways cybercriminals abuse stolen usernames and passwords. This is a brute-force attack technique, but instead of trying to guess passwords using “dictionaries” of common word combinations, attackers use lists of known valid credentials obtained from data breaches.
Credential stuffing attacks are very effective because many people use the same password or a few variations of it for multiple online accounts. According to a study by Google, 52% of users reuse the same password for multiple accounts and 13% of users reuse the same password for all their accounts. This means that if one of your accounts is compromised in a data breach, all your other accounts that use the same password are at risk of being hacked as well.
How Does Credential Stuffing Work?
Credential stuffing attacks usually follow these steps:
- The attacker obtains a list of email addresses and passwords from a data breach or other sources. These lists are often sold or shared on the dark web or hacking forums.
- The attacker uses a tool or a botnet to automate the process of trying different combinations of usernames and passwords on various websites. The tool or botnet can bypass security measures such as CAPTCHAs or rate limits by using proxies or rotating IP addresses.
- The attacker identifies which credentials are valid for each website and collects them in a database. The attacker can then use these credentials to access the user’s account, steal personal information, perform fraudulent transactions, send spam, or launch further attacks.
How Can You Prevent Credential Stuffing?
The best way to prevent credential stuffing attacks is to use strong, unique passwords for every online account. A strong password is one that is long, complex, and random, and that does not contain any personal or common information. A unique password is one that is not used for any other account or service.
To create and manage strong, unique passwords, you can use a password manager. A password manager is a software application that securely stores your passwords and generates new ones for you. You only need to remember one master password to access your password manager and all your other passwords.
Another way to prevent credential stuffing attacks is to use services such as HaveIBeenPwned. HaveIBeenPwned is a website that allows you to check if your email address or password has been exposed in a data breach. You can also subscribe to receive notifications if your email address appears in future breaches. If you find out that your email address or password has been compromised, you should change it immediately and check your other accounts for suspicious activity.
Additionally, you can enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for your online accounts whenever possible. MFA is a security feature that requires you to provide more than one piece of evidence to verify your identity when logging in. For example, you may need to enter a code sent to your phone or email, scan your fingerprint, or use an app like Google Authenticator. MFA adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts and makes it harder for hackers to access them even if they have your credentials.
Conclusion
Credential stuffing is a serious cyberattack that exploits the password reuse problem. It can result in identity theft, financial loss, privacy violation, and other damages. To protect yourself from credential stuffing attacks, you should use services such as HaveIBeenPwned to check if your credentials have been exposed in data breaches, use strong, unique passwords for every online account, use a password manager to create and manage your passwords, and enable multi-factor authentication for your accounts.
By following these tips, you can improve your online security and reduce the risk of credential stuffing attacks.
Enhanced Password Standards: Strengthening Security at TRU
Vivian Oosthoek, Oct 10, 2023
At Thompson Rivers University (TRU), we are committed to safeguarding your digital security. As part of our ongoing efforts to protect your personal information and ensure the integrity of our systems, we are proud to announce significant updates to our password standards, effective as of August of this year. These changes are designed to enhance your online safety and minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Key Updates to Password Standards:
- Increased Minimum Password Length: We've raised the bar for password complexity by increasing the minimum password length from 8 characters to a more robust 12 characters. This longer character requirement helps create stronger, more resilient passwords.
- Comprehensive Character Requirements: To further fortify your passwords, we now mandate the use of a combination of lowercase letters, uppercase letters, numeric digits, and symbol characters. This diverse mix of characters makes it considerably more challenging for unauthorized parties to crack your password.
- Elimination of Regular Expirations: In our commitment to user convenience, we have eliminated the routine password expiration policy, as we now have MFA as a secondary layer of protection against account compromise. Your password will only expire if your account is implicated in a security incident. Previously, staff members were required to update their passwords every 6 months, while students had to do so annually. Now, you'll only need to update your password if there's a legitimate security concern.
Why These Changes Matter:
These updates reflect our commitment to continuously improving your digital security. Passwords serve as the first line of defense against cyber threats, and by strengthening our password standards, we reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. These measures not only protect you but also contribute to a safer and more secure digital environment for our entire TRU community.
At TRU, your online safety is our top priority. Our enhanced password standards, including increased complexity requirements and the elimination of regular expirations, are designed to provide you with peace of mind when it comes to protecting your digital identity and sensitive information.
Enhancing TRU's Security with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Taylar Masson, Oct 10, 2023
We are excited to announce an important security enhancement for your accounts at TRU. Recently, we have enabled Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all student accounts accessing Microsoft services, including email and the Office suite. In this blog post, we will explain what MFA is, why it matters, how we are implementing it, and where you can find resources to manage your account effectively.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
MFA is a security feature that adds an extra layer of protection to your account. Instead of relying solely on a password, MFA requires you to provide an additional form of verification during sign-in. This could be a text message code, a phone call, or a mobile app notification. By using MFA, we significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access even if your password is compromised.
Why is MFA Important?
- Enhanced Security: With MFA, even if someone gets hold of your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second factor (e.g., your phone).
- Protection Against Phishing: MFA prevents attackers from gaining access through phishing attacks.
- Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory standards now mandate the use of MFA to protect sensitive data.
How We are Implementing MFA
Enforced for All Students
- MFA is now mandatory for all TRU student accounts. When you sign into Microsoft services, you will be prompted to set up MFA. This added layer of security ensures that even if your password is compromised, unauthorized access is prevented.
Where MFA Is Needed
- On-Campus Access: When signing in from TRU campus locations, MFA will not be mandatory.
- Off-Campus Access: For security reasons, MFA remains enforced when accessing your account remotely.
Easy Setup
- Setting up MFA is straightforward:
- Sign into any Microsoft service (e.g., Outlook, Teams).
- Follow the prompts to choose your preferred verification method:
- Text message
- Phone call
- Mobile app notification
- Complete the setup process.
Remember Your Device
- Once you have set up MFA on a device (e.g., laptop, smartphone), you will not need to verify again unless you switch to a new device, browser, or have been inactive for more than a month.
- Remember that this convenience also means safeguarding your device against unauthorized use.
Managing Your Account
- To set up or manage student MFA settings: https://aka.ms/mfasetup
- For any issues or questions related to MFA: Contact our IT support team at itservicedesk@tru.ca
- Learn more about MFA: Visit our MFA Knowledge Base https://tru.teamdynamix.com/TDClient/84/Portal/KB/ArticleDet?ID=6714
Upcoming Changes
As part of our commitment to enhancing the security of our digital environment, we plan to extend MFA to other key services soon. Here is what you can expect:
Moodle
Our Learning Management System, Moodle, will soon require MFA for sign-in. This will ensure that only you can access your courses, grades, and other academic resources.
MYTRU
MyTRU, your portal for registration, financial aid, personal information, and other student services, will also be adopting MFA. This will add an extra layer of protection to your personal and academic records.
VPN
For those who access our network remotely via VPN, MFA will be implemented to prevent unauthorized access. This is especially important as VPN provides access to internal resources that are otherwise inaccessible from outside our network.
Passwordless Authentication
- Your Microsoft account offers what is called “Passwordless sign-in". For those with Microsoft MFA setup on the Microsoft Authenticator you can enable this option in the App. You may also elect to add a hardware token to use this (Such as a “Yubikey”).
- Passwordless authentication lets you sign in, as it suggests, without using your password. Having your phone (Something you have), combined with biometrics (Something you are) or PIN code (Something you know) cover the “multiple factors” in MFA and is more secure than a password, which could be easily guessed or stolen.
- DUO MFA for employees does not currently support this. This option will become available in the near future.
You will not have to do anything as part of these changes. All services will use your Microsoft account and be protected by the same MFA you set up now.
Remember that security is a shared responsibility. By using MFA, you play an active role in safeguarding your account and our institution’s data.
Thank you for helping us create a more secure digital environment at TRU!
Embrace the Power of VPNs - but Beware of the Slow Lane
Obiora Akachukwu, October 10, 2023
We live in an age where staying connected is crucial, and that often means hopping onto public Wi-Fi networks. Whether you're at a coffee shop, the library, or an airport, free public Wi-Fi is a lifesaver. But it comes with risks—risks that can be mitigated with a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over the internet, allowing users to access the internet as if they were connected to a private network. A VPN is like your own secret tunnel in the digital world.
Let's dive into the benefits of incorporating VPNs into your online routine.
Benefits
- Enhanced Privacy and Security
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
- Secure File Sharing
- Anonymity and Reduced Tracking
- Access to Institutional Resources
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, making it incredibly difficult for hackers or prying eyes to intercept your online activities. This is particularly valuable when accessing public Wi-Fi networks, which are notorious for their lack of security. For students and faculty handling sensitive academic data, this level of protection is a game-changer.
VPNs allow you to appear as though you're browsing the internet from a different location. This means you can access online resources or educational content that may be restricted or blocked in your region, broadening your research and learning possibilities.
VPNs create a secure tunnel for data transfer, making file sharing and collaboration safer and more confidential. This is particularly useful for faculty members working on research projects or students engaged in group assignments.
VPNs mask your IP address, reducing the ability of websites and advertisers to track your online behavior. This can enhance your online privacy and reduce the amount of targeted advertising you encounter.
Universities and colleges like TRU sometimes limit access to their resources from off-campus locations. A VPN can provide a secure way to connect to the university's network remotely, giving faculty and students access to library resources, academic databases, and other services even when not on campus. TRU offers access to the GlobalProtect VPN for this very purpose.
In conclusion, VPNs offer valuable advantages for both students and faculty, especially when it comes to online security and privacy. However, they are not without their drawbacks, including potential speed reductions and the need to trust a third-party provider when not using the university-provided VPN solution. When deciding whether to use a VPN, consider your specific needs and the potential benefits and limitations in the context of your online activities.
Protect Your Identity Information!
Kevin Zhong, Oct 10, 2023
Identity theft happens when someone uses your personal data, such as your name, birthday, social insurance number, to impersonate you. Identity thieves may steal money from your bank accounts, open new credit cards, or get utility services under your name, steal your tax refund, use your insurance information to receive medical treatments, or give police your name and address when they are arrested.
There are ways to protect yourself from identity theft:
- Change your password regularly and use two-factor authentication.
- Do not keep extra credit cards, or your Social Insurance Card, birth certificate, or passport with you unless necessary.
- Freeze your credit with the two major credit bureaus in Canada, Equifax and TransUnion, so that most lenders cannot obtain your credit report, therefore new credit files cannot be opened under your identity. It is free to freeze and unfreeze your credit.
- Keep a list of all your credit and bank accounts in a secure place so you can quickly call the issuers to inform them about missing or stolen cards. Your list should include account numbers, expiration dates, and customer service and fraud department telephone numbers.
- Take your credit/debit and ATM card receipts with you. Do not toss them and pre-approved credit offers, credit card or utility bills in your trash or recycling bin without first tearing them into small pieces or shredding them.
- Do not give credit card, bank, or Social Insurance Number information to anyone by telephone, even if you made the call, until you can verify that the call is legitimate.
- Avoid any offer that sounds too good to be true – they are often scams. Be very skeptical of offers that require your Social Insurance Number, credit, or financial information as an enrollment condition.
How do I know if I’m a victim of identity theft?
- Scrutinize your credit card statement, utility, and subscription bills to ensure the charges are yours.
- One of your creditors informs you that they have approved or declined your application that you have never applied for.
- A collection agency contacts you to collect on your defaulted account, when you never opened that account.
What should I do if I suspect that I’m a victim of credit fraud?
- Reconcile your cheque and credit card statements regularly and challenge any purchases you did not make.
- Report all stolen credit cards immediately to the issuers and request new cards.
- If you are a victim of a data breach, ask the credit bureaus (Equifax and TransUnion in Canada) to place a fraud alert on your credit files. Lenders will need to contact you and confirm your identity before they approve any application for credit under your identity.
- Contact your local police to file a complaint after a data breach.
- Report any fraud to the Canadian Anti-Fraud Center (CAFC). The CAFC is a national police service that assists Police of Jurisdiction. It is Canada’s central repository for information about fraud.
- Notify Canada Post Postal Security if you suspect your mail was stolen.
Week 1 of Cybersecurity Awareness Month
Blocking Spam and Protecting Your University Inbox: The Power of Microsoft Spam Filtering and DMARC
Obiora Akachukwu, Oct 3, 2023
Today, let’s chat about something that's both annoying and potentially harmful: spam emails.
In June of 2023, the Information Technology Services implemented Microsoft's advanced spam filtering technology and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) to make our university email experience way safer and smoother. Let's dive into the world of these new email standards and see how they're protecting our inboxes.
1. Microsoft Spam Filtering: Your Email Bouncer
You know those pesky spam emails that clutter your inbox? They're like party crashers at your favorite hangout. Microsoft's spam filtering technology is like the bouncer who keeps the undesirables out. It uses smart algorithms to spot spammy emails and sends them straight to the digital trash bin. No more sifting through shady promotions or suspicious offers.
2. DMARC: The Ultimate Identity Checker
DMARC is like the digital passport control at the airport but for emails. It helps ensure that the emails you receive are from who they claim to be from. Cybercriminals often try to impersonate trusted sources, like your employer, to trick you into revealing sensitive information. DMARC verifies the authenticity of the sender's domain, making it much harder for email scammers to sneak in.
3. Reduced Phishing Risks
Phishing attacks are like digital fishing expeditions where scammers try to hook you with fake emails. These can be seriously dangerous, especially for students and faculty dealing with academic and personal data. Microsoft's spam filtering and DMARC combo work together to spot phishing emails and protect your personal info and login credentials.
4. Enhanced Email Security
In the age of cyber threats, keeping your email secure is a top priority. Microsoft's robust spam filtering technology and DMARC help guard our university communications like a fortress. You can collaborate, share research, and communicate without worrying about email security breaches.
So, there you have it, folks. Microsoft's spam filtering technology and DMARC are like the dynamic duo of email security, making sure your university inbox is clean, safe, and hassle-free. You can focus on your studies, research, and teaching without spending as much time worrying about the distraction of spam or the fear of email scams. It's like having a digital guardian for your university email, which is a great perk.
ChatGPT - Protecting your Privacy
Kevin Zhong, Oct 3, 2023
Is using ChatGPT private? The answer is no, ChatGPT is not private. Information entered into ChatGPT is stored on OpenAI’s servers and used to further train the AI tool. Users should exercise caution and not enter confidential or personal information into ChatGPT. According to OpenAI’s privacy policy, collected personal information related to you includes:
- Account and Communication Information: OpenAI collects your name, contact information, payment card information, and transaction history from your user account. If you communicate with OpenAI about any issue, they also collect the contents of any messages you send to them.
- User Content: When you use OpenAI Services, they collect personal information that is included in the input, file uploads, or feedback that you provide.
- Social Media Information: When you interact with OpenAI social media pages on popular social media platforms, such as Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, they will collect personal information that you elect to provide to them.
- Log Data: Information that your browser automatically sends when you use OpenAI Services. Log data includes your Internet Protocol address, browser type and settings, the date and time of your request, and how you interact with their website.
- Usage Data: ChatGPT may automatically collect information about your use of the Services, such as the types of content that you view or engage with, the features you use and the actions you take, as well as your time zone, country, the dates and times of access, user agent and version, type of computer or mobile device, and your computer connection.
- Device Information: This can include the name of the device, the operating system, device identifiers, and the browser you are using.
- Cookies and Analytics: OpenAI uses a variety of online analytics products that use cookies to help them analyze how you use their services.
So, how should you protect your privacy when using ChatGPT?
- Don’t share sensitive information: confidential information should not be entered into ChatGPT.
- Use a VPN to increase your anonymity.
- Disabling your chat history through your account settings does not prevent the use of your data in training ChatGPT. However, you can fill out the OpenAI “User Content Opt Out Request” Google form to opt out of having your data used to improve their language models.
